Equations and Inequalities with Absolute Value
Learning Objectives
- Solve equations containing absolute values
- Recognize when a linear equation that contains absolute value does not have a solution
- Solve inequalities containing absolute values
Solving an Absolute Value Equation
Next, we will learn how to slve an absolute value equation. To solve an equation such as [latex]|2x - 6|=8[/latex], we notice that the absolute value will be equal to 8 if the quantity inside the absolute value bars is [latex]8[/latex] or [latex]-8[/latex]. This leads to two different equations we can solve independently.A General Note: Absolute Value Equations
The absolute value of x is written as [latex]|x|[/latex]. It has the following properties:How To: Given an absolute value equation, solve it.
- Isolate the absolute value expression on one side of the equal sign.
- If [latex]c>0[/latex], write and solve two equations: [latex]ax+b=c[/latex] and [latex]ax+b=-c[/latex].
Example: Solving Absolute Value Equations
Solve the following absolute value equations:- [latex]|6x+4|=8[/latex]
- [latex]|3x+4|=-9[/latex]
- [latex]|3x - 5|-4=6[/latex]
- [latex]|-5x+10|=0[/latex]
Answer: a. [latex]|6x+4|=8[/latex] Write two equations and solve each:
[latex]\begin{array}{ll}6x+4\hfill&=8\hfill& 6x+4\hfill&=-8\hfill \\ 6x\hfill&=4\hfill& 6x\hfill&=-12\hfill \\ x\hfill&=\frac{2}{3}\hfill& x\hfill&=-2\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
The two solutions are [latex]x=\frac{2}{3}[/latex], [latex]x=-2[/latex]. b. [latex]|3x+4|=-9[/latex] There is no solution as an absolute value cannot be negative. c. [latex]|3x - 5|-4=6[/latex] Isolate the absolute value expression and then write two equations.Try It
Solve the absolute value equation: [latex]|1 - 4x|+8=13[/latex].Answer: [latex]x=-1[/latex], [latex]x=\frac{3}{2}[/latex]
Absolute value equations with no solutions
As we are solving absolute value equations it is important to be aware of special cases. An absolute value is defined as the distance from 0 on a number line, so it must be a positive number. When an absolute value expression is equal to a negative number, we say the equation has no solution, or DNE. Notice how this happens in the next two examples.Example
Solve for x. [latex]7+\left|2x-5\right|=4[/latex]Answer: Notice absolute value is not alone. Subtract [latex]7[/latex] from each side to isolate the absolute value.
[latex]\begin{array}{r}7+\left|2x-5\right|=4\,\,\,\,\\\underline{\,-7\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-7\,}\\\left|2x-5\right|=-3\end{array}[/latex]
Result of absolute value is negative! The result of an absolute value must always be positive, so we say there is no solution to this equation, or DNE.Example
Solve for x. [latex]-\frac{1}{2}\left|x+3\right|=6[/latex]Answer: Notice absolute value is not alone, multiply both sides by the reciprocal of [latex]-\frac{1}{2}[/latex], which is [latex]-2[/latex].
[latex]\begin{array}{r}-\frac{1}{2}\left|x+3\right|=6\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left(-2\right)-\frac{1}{2}\left|x+3\right|=\left(-2\right)6\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left|x+3\right|=-12\,\,\,\,\,\end{array}[/latex]
Again, we have a result where an absolute value is negative! There is no solution to this equation, or DNE.Solve inequalities containing absolute values
Let’s apply what you know about solving equations that contain absolute values and what you know about inequalities to solve inequalities that contain absolute values. Let’s start with a simple inequality.[latex]\left|x\right|\leq 4[/latex]
This inequality is read, “the absolute value of x is less than or equal to 4.” If you are asked to solve for x, you want to find out what values of x are 4 units or less away from 0 on a number line. You could start by thinking about the number line and what values of x would satisfy this equation. 4 and [latex]−4[/latex] are both four units away from 0, so they are solutions. 3 and [latex]−3[/latex] are also solutions because each of these values is less than 4 units away from 0. So are 1 and [latex]−1[/latex], 0.5 and [latex]−0.5[/latex], and so on—there are an infinite number of values for x that will satisfy this inequality. The graph of this inequality will have two closed circles, at 4 and [latex]−4[/latex]. The distance between these two values on the number line is colored in blue because all of these values satisfy the inequality. The solution can be written this way:
Inequality: [latex]-4\leq x\leq4[/latex]
Interval: [latex]\left[-4,4\right][/latex]
The situation is a little different when the inequality sign is “greater than” or “greater than or equal to.” Consider the simple inequality [latex]\left|x\right|>3[/latex]. Again, you could think of the number line and what values of x are greater than 3 units away from zero. This time, 3 and [latex]−3[/latex] are not included in the solution, so there are open circles on both of these values. 2 and [latex]−2[/latex] would not be solutions because they are not more than 3 units away from 0. But 5 and [latex]−5[/latex] would work, and so would all of the values extending to the left of [latex]−3[/latex] and to the right of 3. The graph would look like the one below.
The solution can be written this way:
Inequality: [latex]-4\leq x\leq4[/latex]
Interval: [latex]\left[-4,4\right][/latex]
The situation is a little different when the inequality sign is “greater than” or “greater than or equal to.” Consider the simple inequality [latex]\left|x\right|>3[/latex]. Again, you could think of the number line and what values of x are greater than 3 units away from zero. This time, 3 and [latex]−3[/latex] are not included in the solution, so there are open circles on both of these values. 2 and [latex]−2[/latex] would not be solutions because they are not more than 3 units away from 0. But 5 and [latex]−5[/latex] would work, and so would all of the values extending to the left of [latex]−3[/latex] and to the right of 3. The graph would look like the one below.
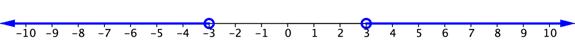 The solution to this inequality can be written this way:
Inequality: [latex]x<−3[/latex] or [latex]x>3[/latex].
Interval: [latex]\left(-\infty, -3\right)\cup\left(3,\infty\right)[/latex]
In the following video, you will see examples of how to solve and express the solution to absolute value inequalities involving both AND and OR.
https://youtu.be/0cXxATY2S-k
The solution to this inequality can be written this way:
Inequality: [latex]x<−3[/latex] or [latex]x>3[/latex].
Interval: [latex]\left(-\infty, -3\right)\cup\left(3,\infty\right)[/latex]
In the following video, you will see examples of how to solve and express the solution to absolute value inequalities involving both AND and OR.
https://youtu.be/0cXxATY2S-k
Writing Solutions to Absolute Value Inequalities
For any positive value of a and x, a single variable, or any algebraic expression:| Absolute Value Inequality | Equivalent Inequality | Interval Notation |
| [latex]\left|{ x }\right|\le{ a}[/latex] | [latex]{ -a}\le{x}\le{ a}[/latex] | [latex]\left[-a, a\right][/latex] |
| [latex]\left| x \right|\lt{a}[/latex] | [latex]{ -a}\lt{x}\lt{ a}[/latex] | [latex]\left(-a, a\right)[/latex] |
| [latex]\left| x \right|\ge{ a}[/latex] | [latex]{x}\le\text{−a}[/latex] or [latex]{x}\ge{ a}[/latex] | [latex]\left(-\infty,-a\right]\cup\left[a,\infty\right)[/latex] |
| [latex]\left| x \right|\gt\text{a}[/latex] | [latex]\displaystyle{x}\lt\text{−a}[/latex] or [latex]{x}\gt{ a}[/latex] | [latex]\left(-\infty,-a\right)\cup\left(a,\infty\right)[/latex] |
Example
Solve for x. [latex]\left|x+3\right|\gt4[/latex]Answer: Since this is a “greater than” inequality, the solution can be rewritten according to the “greater than” rule.
[latex] \displaystyle x+3<-4\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\text{or}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,x+3>4[/latex]
Solve each inequality.[latex]\begin{array}{r}x+3<-4\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,x+3>4\\\underline{\,\,\,\,-3\,\,\,\,\,-3}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,-3\,\,-3}\\x\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,<-7\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,x\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,>1\\\\x<-7\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\text{or}\,\,\,\,\,\,x>1\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\end{array}[/latex]
Check the solutions in the original equation to be sure they work. Check the end point of the first related equation, [latex]−7[/latex] and the end point of the second related equation, 1.[latex] \displaystyle \begin{array}{r}\,\,\,\left| x+3 \right|>4\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left| x+3 \right|>4\\\left| -7+3 \right|=4\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left| 1+3 \right|=4\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left| -4 \right|=4\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left| 4 \right|=4\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,4=4\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,4=4\end{array}[/latex]
Try [latex]−10[/latex], a value less than [latex]−7[/latex], and 5, a value greater than 1, to check the inequality.[latex] \displaystyle \begin{array}{r}\,\,\,\,\,\left| x+3 \right|>4\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left| x+3 \right|>4\\\left| -10+3 \right|>4\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left| 5+3 \right|>4\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left| -7 \right|>4\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left| 8 \right|>4\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,7>4\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,8>4\end{array}[/latex]
Both solutions check!Answer
Inequality: [latex] \displaystyle x<-7\,\,\,\,\,\text{or}\,\,\,\,\,x>1[/latex] Interval: [latex]\left(-\infty, -7\right)\cup\left(1,\infty\right)[/latex] Graph: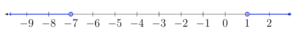
Example
Solve for y. [latex] \displaystyle \mathsf{3}\left| \mathsf{2}\mathrm{y}\mathsf{+6} \right|-\mathsf{9<27}[/latex]Answer: Begin to isolate the absolute value by adding 9 to both sides of the inequality.
[latex] \displaystyle \begin{array}{r}3\left| 2y+6 \right|-9<27\\\underline{\,\,+9\,\,\,+9}\\3\left| 2y+6 \right|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,<36\end{array}[/latex]
Divide both sides by 3 to isolate the absolute value.[latex]\begin{array}{r}\underline{3\left| 2y+6 \right|}\,<\underline{36}\\3\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,3\,\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left| 2y+6 \right|<12\end{array}[/latex]
Write the absolute value inequality using the “less than” rule. Subtract 6 from each part of the inequality.[latex]\begin{array}{r}-12<2y+6<12\\\underline{\,\,-6\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-6\,\,\,-6}\\-18\,<\,2y\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,<\,\,6\,\end{array}[/latex]
Divide by 2 to isolate the variable.[latex]\begin{array}{r}\underline{-18}<\underline{2y}<\underline{\,6\,}\\2\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,2\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,2\,\,\\-9<\,\,y\,\,\,\,<\,3\end{array}[/latex]
Answer
Inequality: [latex] \displaystyle -9<\,\,y\,\,<3[/latex] Interval: [latex]\left(-9,3\right)[/latex] Graph:
Identify cases of inequalities containing absolute values that have no solutions
As with equations, there may be instances in which there is no solution to an inequality.Example
Solve for x. [latex]\left|2x+3\right|+9\leq 7[/latex]Answer: Isolate the absolute value by subtracting 9 from both sides of the inequality.
[latex] \displaystyle \begin{array}{r}\left| 2x+3 \right|+9\,\le \,\,\,7\,\,\\\underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-9\,\,\,\,\,-9}\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left| 2x+3 \right|\,\,\,\le -2\,\end{array}[/latex]
The absolute value of a quantity can never be a negative number, so there is no solution to the inequality.Answer
No solutionSummary
Absolute inequalities can be solved by rewriting them using compound inequalities. The first step to solving absolute inequalities is to isolate the absolute value. The next step is to decide whether you are working with an OR inequality or an AND inequality. If the inequality is greater than a number, we will use OR. If the inequality is less than a number, we will use AND. Remember that if we end up with an absolute value greater than or less than a negative number, there is no solution.Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Ex 1: Solve and Graph Basic Absolute Value inequalities.. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com). License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Ex 2: Solve and Graph Absolute Value inequalities . Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Ex 4: Solve and Graph Absolute Value inequalities (Requires Isolating Abs. Value).. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- College Algebra. . Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Abramson, et al... Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download for free: http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface.
- Ex 4: Solving Absolute Value Equations (Requires Isolating Abs. Value).. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Question ID 60839. Authored by: Alyson Day. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL.
