The First Derivative Test
Learning Objectives
- Explain how the sign of the first derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph.
- State the first derivative test for critical points.
- Find local extrema using the first derivative test.
Earlier in this chapter we stated that if a function [latex]f[/latex] has a local extremum at a point [latex]c[/latex], then [latex]c[/latex] must be a critical point of [latex]f[/latex]. However, a function is not guaranteed to have a local extremum at a critical point. For example, [latex]f(x)=x^3[/latex] has a critical point at [latex]x=0[/latex] since [latex]f^{\prime}(x)=3x^2[/latex] is zero at [latex]x=0[/latex], but [latex]f[/latex] does not have a local extremum at [latex]x=0[/latex]. Using the results from the previous section, we are now able to determine whether a critical point of a function actually corresponds to a local extreme value. In this section, we also see how the second derivative provides information about the shape of a graph by describing whether the graph of a function curves upward or curves downward.
The First Derivative Test
Corollary 3 of the Mean Value Theorem showed that if the derivative of a function is positive over an interval [latex]I[/latex] then the function is increasing over [latex]I[/latex]. On the other hand, if the derivative of the function is negative over an interval [latex]I[/latex], then the function is decreasing over [latex]I[/latex] as shown in the following figure.
 Figure 1. Both functions are increasing over the interval [latex](a,b)[/latex]. At each point [latex]x[/latex], the derivative [latex]f^{\prime}(x)>0[/latex]. Both functions are decreasing over the interval [latex](a,b)[/latex]. At each point [latex]x[/latex], the derivative [latex]f^{\prime}(x)<0[/latex].
Figure 1. Both functions are increasing over the interval [latex](a,b)[/latex]. At each point [latex]x[/latex], the derivative [latex]f^{\prime}(x)>0[/latex]. Both functions are decreasing over the interval [latex](a,b)[/latex]. At each point [latex]x[/latex], the derivative [latex]f^{\prime}(x)<0[/latex].A continuous function [latex]f[/latex] has a local maximum at point [latex]c[/latex] if and only if [latex]f[/latex] switches from increasing to decreasing at point [latex]c[/latex]. Similarly, [latex]f[/latex] has a local minimum at [latex]c[/latex] if and only if [latex]f[/latex] switches from decreasing to increasing at [latex]c[/latex]. If [latex]f[/latex] is a continuous function over an interval [latex]I[/latex] containing [latex]c[/latex] and differentiable over [latex]I[/latex], except possibly at [latex]c[/latex], the only way [latex]f[/latex] can switch from increasing to decreasing (or vice versa) at point [latex]c[/latex] is if [latex]{f}^{\prime }[/latex] changes sign as [latex]x[/latex] increases through [latex]c.[/latex] If [latex]f[/latex] is differentiable at [latex]c,[/latex] the only way that [latex]{f}^{\prime }.[/latex] can change sign as [latex]x[/latex] increases through [latex]c[/latex] is if [latex]f^{\prime}(c)=0[/latex]. Therefore, for a function [latex]f[/latex] that is continuous over an interval [latex]I[/latex] containing [latex]c[/latex] and differentiable over [latex]I[/latex], except possibly at [latex]c[/latex], the only way [latex]f[/latex] can switch from increasing to decreasing (or vice versa) is if [latex]f^{\prime}(c)=0[/latex] or [latex]f^{\prime}(c)[/latex] is undefined. Consequently, to locate local extrema for a function [latex]f[/latex], we look for points [latex]c[/latex] in the domain of [latex]f[/latex] such that [latex]f^{\prime}(c)=0[/latex] or [latex]f^{\prime}(c)[/latex] is undefined. Recall that such points are called critical points of [latex]f[/latex].
Note that [latex]f[/latex] need not have a local extrema at a critical point. The critical points are candidates for local extrema only. In (Figure), we show that if a continuous function [latex]f[/latex] has a local extremum, it must occur at a critical point, but a function may not have a local extremum at a critical point. We show that if [latex]f[/latex] has a local extremum at a critical point, then the sign of [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] switches as [latex]x[/latex] increases through that point. Figure 2. The function [latex]f[/latex] has four critical points: [latex]a,b,c[/latex], and [latex]d[/latex]. The function [latex]f[/latex] has local maxima at [latex]a[/latex] and [latex]d[/latex], and a local minimum at [latex]b[/latex]. The function [latex]f[/latex] does not have a local extremum at [latex]c[/latex]. The sign of [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] changes at all local extrema.
Figure 2. The function [latex]f[/latex] has four critical points: [latex]a,b,c[/latex], and [latex]d[/latex]. The function [latex]f[/latex] has local maxima at [latex]a[/latex] and [latex]d[/latex], and a local minimum at [latex]b[/latex]. The function [latex]f[/latex] does not have a local extremum at [latex]c[/latex]. The sign of [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] changes at all local extrema.Using (Figure), we summarize the main results regarding local extrema.
- If a continuous function [latex]f[/latex] has a local extremum, it must occur at a critical point [latex]c[/latex].
- The function has a local extremum at the critical point [latex]c[/latex] if and only if the derivative [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] switches sign as [latex]x[/latex] increases through [latex]c[/latex].
- Therefore, to test whether a function has a local extremum at a critical point [latex]c[/latex], we must determine the sign of [latex]f^{\prime}(x)[/latex] to the left and right of [latex]c[/latex].
This result is known as the first derivative test.
First Derivative Test
Suppose that [latex]f[/latex] is a continuous function over an interval [latex]I[/latex] containing a critical point [latex]c[/latex]. If [latex]f[/latex] is differentiable over [latex]I[/latex], except possibly at point [latex]c[/latex], then [latex]f(c)[/latex] satisfies one of the following descriptions:
- If [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] changes sign from positive when [latex]x<c[/latex] to negative when [latex]x>c[/latex], then [latex]f(c)[/latex] is a local maximum of [latex]f[/latex].
- If [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] changes sign from negative when [latex]x<c[/latex] to positive when [latex]x>c[/latex], then [latex]f(c)[/latex] is a local minimum of [latex]f[/latex].
- If [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] has the same sign for [latex]x<c[/latex] and [latex]x>c[/latex], then [latex]f(c)[/latex] is neither a local maximum nor a local minimum of [latex]f[/latex].
We can summarize the first derivative test as a strategy for locating local extrema.
Problem-Solving Strategy: Using the First Derivative Test
Consider a function [latex]f[/latex] that is continuous over an interval [latex]I[/latex].
- Find all critical points of [latex]f[/latex] and divide the interval [latex]I[/latex] into smaller intervals using the critical points as endpoints.
- Analyze the sign of [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] in each of the subintervals. If [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] is continuous over a given subinterval (which is typically the case), then the sign of [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] in that subinterval does not change and, therefore, can be determined by choosing an arbitrary test point [latex]x[/latex] in that subinterval and by evaluating the sign of [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] at that test point. Use the sign analysis to determine whether [latex]f[/latex] is increasing or decreasing over that interval.
- Use (Figure) and the results of step 2 to determine whether [latex]f[/latex] has a local maximum, a local minimum, or neither at each of the critical points.
Using the First Derivative Test to Find Local Extrema
Answer:
Step 1. The derivative is [latex]f^{\prime}(x)=3x^2-6x-9[/latex]. To find the critical points, we need to find where [latex]f^{\prime}(x)=0[/latex]. Factoring the polynomial, we conclude that the critical points must satisfy
Therefore, the critical points are [latex]x=3,-1[/latex]. Now divide the interval [latex](−\infty ,\infty)[/latex] into the smaller intervals [latex](−\infty ,-1), \, (-1,3)[/latex], and [latex](3,\infty)[/latex].
Step 2. Since [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] is a continuous function, to determine the sign of [latex]f^{\prime}(x)[/latex] over each subinterval, it suffices to choose a point over each of the intervals [latex](−\infty ,-1), \, (-1,3)[/latex], and [latex](3,\infty)[/latex] and determine the sign of [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] at each of these points. For example, let’s choose [latex]x=-2, \, x=0[/latex], and [latex]x=4[/latex] as test points.
| Interval | Test Point | Sign of [latex]f^{\prime}(x)=3(x-3)(x+1)[/latex] at Test Point | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| [latex](−\infty ,-1)[/latex] | [latex]x=-2[/latex] | [latex](+)(−)(−)=+[/latex] | [latex]f[/latex] is increasing. |
| [latex](-1,3)[/latex] | [latex]x=0[/latex] | [latex](+)(−)(+)=−[/latex] | [latex]f[/latex] is decreasing. |
| [latex](3,\infty)[/latex] | [latex]x=4[/latex] | [latex](+)(+)(+)=+[/latex] | [latex]f[/latex] is increasing. |
Step 3. Since [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] switches sign from positive to negative as [latex]x[/latex] increases through [latex]1, \, f[/latex] has a local maximum at [latex]x=-1[/latex]. Since [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] switches sign from negative to positive as [latex]x[/latex] increases through [latex]3, \, f[/latex] has a local minimum at [latex]x=3[/latex]. These analytical results agree with the following graph.
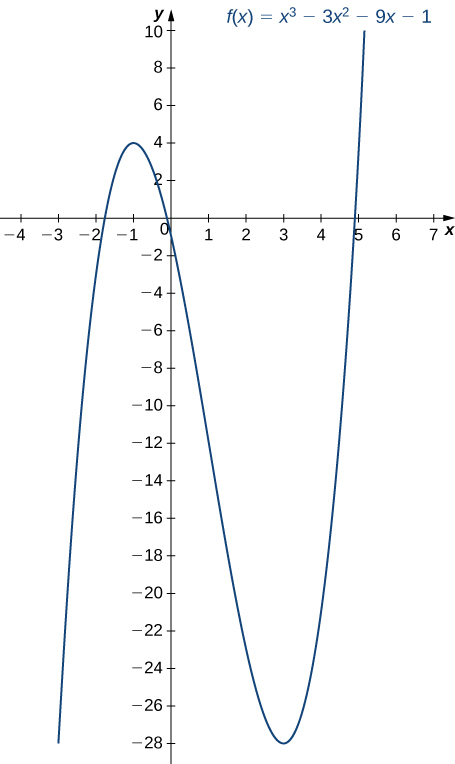 Figure 3. The function [latex]f[/latex] has a maximum at [latex]x=-1[/latex] and a minimum at [latex]x=3[/latex]
Figure 3. The function [latex]f[/latex] has a maximum at [latex]x=-1[/latex] and a minimum at [latex]x=3[/latex]Use the first derivative test to locate all local extrema for [latex]f(x)=−x^3+\frac{3}{2}x^2+18x[/latex].
Answer:
[latex]f[/latex] has a local minimum at -2 and a local maximum at 3.
Using the First Derivative Test
Use the first derivative test to find the location of all local extrema for [latex]f(x)=5x^{1/3}-x^{5/3}[/latex]. Use a graphing utility to confirm your results.
Answer:
Step 1. The derivative is
Step 2: Since [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] is continuous over each subinterval, it suffices to choose a test point [latex]x[/latex] in each of the intervals from step 1 and determine the sign of [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] at each of these points. The points [latex]x=-2, \, x=-\frac{1}{2}, \, x=\frac{1}{2}[/latex], and [latex]x=2[/latex] are test points for these intervals.
| Interval | Test Point | Sign of [latex]f^{\prime}(x)=\frac{5(1-x^{4/3})}{3x^{2/3}}[/latex] at Test Point | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| [latex](−\infty ,-1)[/latex] | [latex]x=-2[/latex] | [latex]\frac{(+)(−)}{+}=−[/latex] | [latex]f[/latex] is decreasing. |
| [latex](-1,0)[/latex] | [latex]x=-\frac{1}{2}[/latex] | [latex]\frac{(+)(+)}{+}=+[/latex] | [latex]f[/latex] is increasing. |
| [latex](0,1)[/latex] | [latex]x=\frac{1}{2}[/latex] | [latex]\frac{(+)(+)}{+}=+[/latex] | [latex]f[/latex] is increasing. |
| [latex](1,\infty )[/latex] | [latex]x=2[/latex] | [latex]\frac{(+)(−)}{+}=−[/latex] | [latex]f[/latex] is decreasing. |
Step 3: Since [latex]f[/latex] is decreasing over the interval [latex](−\infty ,-1)[/latex] and increasing over the interval [latex](-1,0)[/latex], [latex]f[/latex] has a local minimum at [latex]x=-1[/latex]. Since [latex]f[/latex] is increasing over the interval [latex](-1,0)[/latex] and the interval [latex](0,1)[/latex], [latex]f[/latex] does not have a local extremum at [latex]x=0[/latex]. Since [latex]f[/latex] is increasing over the interval [latex](0,1)[/latex] and decreasing over the interval [latex](1,\infty ), \, f[/latex] has a local maximum at [latex]x=1[/latex]. The analytical results agree with the following graph.
 Figure 4. The function f has a local minimum at [latex]x=-1[/latex] and a local maximum at [latex]x=1[/latex].
Figure 4. The function f has a local minimum at [latex]x=-1[/latex] and a local maximum at [latex]x=1[/latex].Use the first derivative test to find all local extrema for [latex]f(x)=\sqrt[3]{x-1}[/latex].
Answer:
[latex]f[/latex] has no local extrema because [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] does not change sign at [latex]x=1[/latex].
Hint
The only critical point of [latex]f[/latex] is [latex]x=1[/latex].
Key Concepts
- If [latex]c[/latex] is a critical point of [latex]f[/latex] and [latex]f^{\prime}(x)>0[/latex] for [latex]x<c[/latex] and [latex]f^{\prime}(x)<0[/latex] for [latex]x>c[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] has a local maximum at [latex]c[/latex].
- If [latex]c[/latex] is a critical point of [latex]f[/latex] and [latex]f^{\prime}(x)<0[/latex] for [latex]x<c[/latex] and [latex]f^{\prime}(x)>0[/latex] for [latex]x>c[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] has a local minimum at [latex]c[/latex].
1. If [latex]c[/latex] is a critical point of [latex]f(x)[/latex], when is there no local maximum or minimum at [latex]c[/latex]? Explain.
For the following exercises, analyze the graphs of [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex], then list all intervals where [latex]f[/latex] is increasing or decreasing.
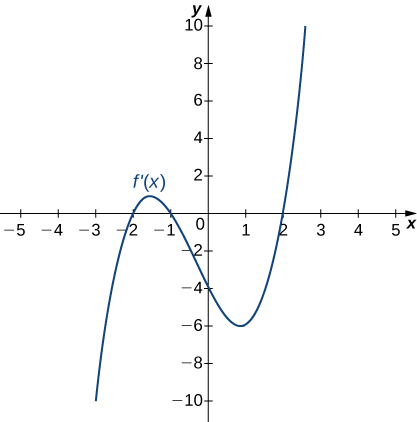
Answer:
Increasing for [latex]-2<x<-1[/latex] and [latex]x>2[/latex]; decreasing for [latex]x<-2[/latex] and [latex]-1<x<2[/latex]
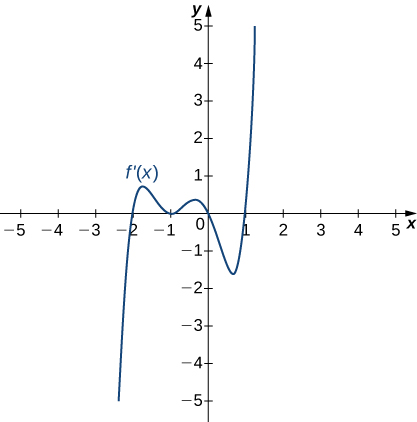
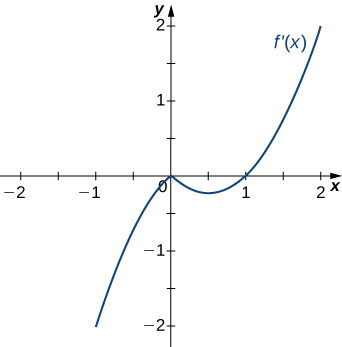
Answer:
Decreasing for [latex]x<1[/latex]; increasing for [latex]x>1[/latex]
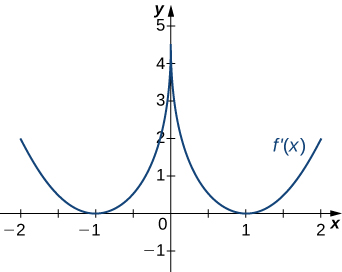
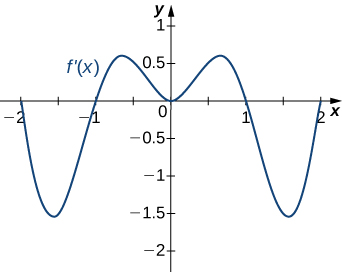
Answer:
Decreasing for [latex]-2<x<-1[/latex] and [latex]1<x<2[/latex]; increasing for [latex]-1<x<1[/latex] and [latex]x<-2[/latex] and [latex]x>2[/latex]
For the following exercises, analyze the graphs of [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex], then list
- all intervals where [latex]f[/latex] is increasing and decreasing and
- where the minima and maxima are located.
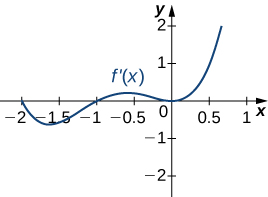
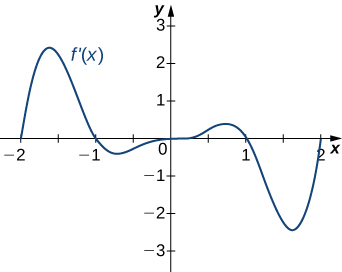
Answer:
a. Increasing over [latex]-2<x<-1, \, 0<x<1, \, x>2[/latex]; decreasing over [latex]x<-2 \, -1<x<0, \, 1<x<2[/latex]; b. maxima at [latex]x=-1[/latex] and [latex]x=1[/latex], minima at [latex]x=-2[/latex] and [latex]x=0[/latex] and [latex]x=2[/latex]
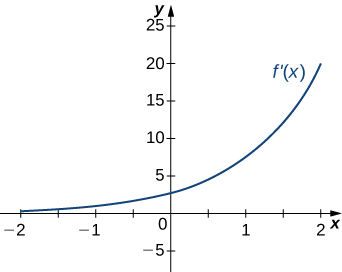
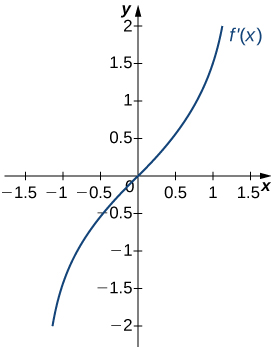
Answer:
a. Increasing over [latex]x>0[/latex], decreasing over [latex]x<0[/latex]; b. Minimum at [latex]x=0[/latex]
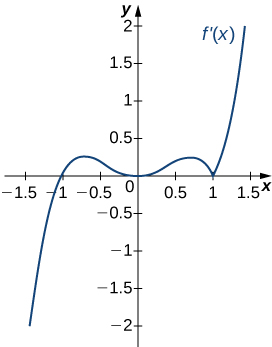
For the following exercises, determine
- intervals where [latex]f[/latex] is increasing or decreasing (in interval notation) and
- local minima and maxima (as a coordinate).
12. [latex]f(x)=-x^2-3x+3[/latex]
Answer:
a. Increasing: [latex]\left(\infty,-\frac{3}{2}\right)[/latex], decreasing: [latex]\left(-\frac{3}{2},\infty\right)[/latex] b. Local maximum at [latex]x=-\frac{3}{2}[/latex]; no local minimum.
13. [latex]f(x)=6x-x^3[/latex]
14. [latex]f(x)=3x^2-4x^3[/latex]
Answer:
a. Increasing: [latex]\left(0,\frac{1}{2}\right)[/latex], decreasing: [latex]\left(-\infty,0\right)\cup\left(\frac{1}{2},\infty\right)[/latex] b. Local maximum at [latex]\left(\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{4}\right)[/latex]; local minimum at [latex](0,0)[/latex].
15. [latex]g(t)=t^4-4t^3+4t^2[/latex]
16. [latex]f(t)=t^4-8t^2+16[/latex]
Answer:
a. Increasing: [latex]\left(-2,0\right)\cup\left(2,\infty\right)[/latex], decreasing: [latex]\left(-\infty,-2\right)\cup\left(0,2\right)[/latex] b. Local maximum at [latex](0,16)[/latex]; local minimums at [latex](-2,0)[/latex] and [latex](2,0)[/latex].
17. [latex]h(x)=4\sqrt{x}-x^2+3[/latex]
18. [latex]h(x)=x-6\sqrt{x-1}[/latex]
Answer:
a. Increasing: [latex]\left(10,\infty\right)[/latex], decreasing: [latex]\left(1,10\right)[/latex] b. No local maximum; local minimum at [latex](10,-8)[/latex].
19. [latex]g(x)=x^{2}\sqrt{5-x}[/latex]
20. [latex]g(x)=x\sqrt{8-x^{2}}[/latex]
Answer:
a. Increasing: [latex]\left(-2,2\right)[/latex], decreasing: [latex]\left(-2\sqrt{2},-2\right)\cup\left(2,2\sqrt{2}\right)[/latex] b. local maximum at [latex]\left(2,4\right)[/latex]; local minimum at [latex]\left(-2,-4\right)[/latex].
21. [latex]f(\theta)=\theta^2 + \cos \theta[/latex]
22. [latex]f(\theta)= \sin \theta+ \sin^3 \theta[/latex] over the interval [latex]\left(-\pi,\pi\right) [/latex]
Answer:
a. Increasing: [latex]\left(-\frac{\pi }{2},\frac{\pi }{2}\right)[/latex], decreasing: [latex]\left(-\pi,-\frac{\pi}{2}\right)\cup\left(\frac{\pi}{2},\pi\right)[/latex] b. Local maximum at [latex]\left(\frac{\pi }{2},2\right)[/latex]; local minimum at [latex]\left(-\frac{\pi }{2},-2\right)[/latex]
23. [latex]f(x)=\frac{x^3}{3x^2+1}[/latex]
24. [latex]f(x)=\frac{x^2-3}{x-2}[/latex]
Answer:
a. Increasing: [latex]\left(-\infty,1\right)[/latex], decreasing: [latex](1,2)\cup(2,3)[/latex] b. local maximum at [latex](1,2)[/latex]; local minimum at [latex](3,6)[/latex].
25. [latex]h(x)=x^{\frac{2}{3}}(x+5)[/latex]
26. [latex]h(x)=x^{\frac{1}{3}}(x+8)[/latex]
Answer:
a. Increasing: [latex]\left(-2,0\right)\cup\left(0,\infty\right)[/latex], decreasing: [latex]\left(-\infty,-2\right)[/latex] b. no local maximum; local minimum at [latex]\left(-2,-6 \sqrt[3]{2}\right)[/latex].
27. [latex]f(x)=e^{\sqrt{x}}[/latex]
28. [latex]f(x)=e^{2x}+e^{-x}[/latex]
Answer:
a. Increasing: [latex]\left(-\frac{\ln(2)}{3},\infty\right)[/latex], decreasing: [latex]\left(-\infty,-\frac{\ln(2)}{3}\right)[/latex] b. no local maximum; local minimum at [latex]\left(-\frac{\ln(2)}{3}, \frac{3\sqrt[3]{2}}{2}\right)[/latex].
29. [latex]f(t)=t^{2}\ln t[/latex]
30. [latex]f(t)=8t \ln t[/latex]
Answer:
a. Increasing: [latex]\left(\frac{1}{e},\infty\right)[/latex], decreasing: [latex]\left(0,\frac{1}{e}\right)[/latex] b. no local maximum; local minimum at [latex]\left(\frac{1}{e}, -\frac{8}{e}\right)[/latex].
Glossary
- concave down
- if [latex]f[/latex] is differentiable over an interval [latex]I[/latex] and [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] is decreasing over [latex]I[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] is concave down over [latex]I[/latex]
- concave up
- if [latex]f[/latex] is differentiable over an interval [latex]I[/latex] and [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] is increasing over [latex]I[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] is concave up over [latex]I[/latex]
- concavity
- the upward or downward curve of the graph of a function
- concavity test
- suppose [latex]f[/latex] is twice differentiable over an interval [latex]I[/latex]; if [latex]f^{\prime \prime}>0[/latex] over [latex]I[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] is concave up over [latex]I[/latex]; if [latex]f^{\prime \prime}<0[/latex] over [latex]I[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] is concave down over [latex]I[/latex]
- first derivative test
- let [latex]f[/latex] be a continuous function over an interval [latex]I[/latex] containing a critical point [latex]c[/latex] such that [latex]f[/latex] is differentiable over [latex]I[/latex] except possibly at [latex]c[/latex]; if [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] changes sign from positive to negative as [latex]x[/latex] increases through [latex]c[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] has a local maximum at [latex]c[/latex]; if [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] changes sign from negative to positive as [latex]x[/latex] increases through [latex]c[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] has a local minimum at [latex]c[/latex]; if [latex]f^{\prime}[/latex] does not change sign as [latex]x[/latex] increases through [latex]c[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] does not have a local extremum at [latex]c[/latex]
- inflection point
- if [latex]f[/latex] is continuous at [latex]c[/latex] and [latex]f[/latex] changes concavity at [latex]c[/latex], the point [latex](c,f(c))[/latex] is an inflection point of [latex]f[/latex]
- second derivative test
- suppose [latex]f^{\prime}(c)=0[/latex] and [latex]f^{\prime \prime}[/latex] is continuous over an interval containing [latex]c[/latex]; if [latex]f^{\prime \prime}(c)>0[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] has a local minimum at [latex]c[/latex]; if [latex]f^{\prime \prime}(c)<0[/latex], then [latex]f[/latex] has a local maximum at [latex]c[/latex]; if [latex]f^{\prime \prime}(c)=0[/latex], then the test is inconclusive
Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Calculus I. Provided by: OpenStax Located at: https://openstax.org/books/calculus-volume-1/pages/1-introduction. License: CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike. License terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected].

Hint
Find all critical points of [latex]f[/latex] and determine the signs of [latex]f^{\prime}(x)[/latex] over particular intervals determined by the critical points.