Identifying Characteristics of Polynomials
Learning Outcomes
- Identify whether a polynomial is a monomial, binomial, or trinomial
- Determine the degree of a polynomial
Identify Polynomials, Monomials, Binomials, and Trinomials
In Evaluate, Simplify, and Translate Expressions, you learned that a term is a constant or the product of a constant and one or more variables. When it is of the form [latex]a{x}^{m}[/latex], where [latex]a[/latex] is a constant and [latex]m[/latex] is a whole number, it is called a monomial. A monomial, or a sum and/or difference of monomials, is called a polynomial.Polynomials
polynomial—A monomial, or two or more monomials, combined by addition or subtraction monomial—A polynomial with exactly one term binomial— A polynomial with exactly two terms trinomial—A polynomial with exactly three terms- poly- means many
- mono- means one
- bi- means two
- tri- means three
| Polynomial | [latex]b+1[/latex] | [latex]4{y}^{2}-7y+2[/latex] | [latex]5{x}^{5}-4{x}^{4}+{x}^{3}+8{x}^{2}-9x+1[/latex] |
| Monomial | [latex]5[/latex] | [latex]4{b}^{2}[/latex] | [latex]-9{x}^{3}[/latex] |
| Binomial | [latex]3a - 7[/latex] | [latex]{y}^{2}-9[/latex] | [latex]17{x}^{3}+14{x}^{2}[/latex] |
| Trinomial | [latex]{x}^{2}-5x+6[/latex] | [latex]4{y}^{2}-7y+2[/latex] | [latex]5{a}^{4}-3{a}^{3}+a[/latex] |
example
Determine whether each polynomial is a monomial, binomial, trinomial, or other polynomial: 1. [latex]8{x}^{2}-7x - 9[/latex] 2. [latex]-5{a}^{4}[/latex] 3. [latex]{x}^{4}-7{x}^{3}-6{x}^{2}+5x+2[/latex] 4. [latex]11 - 4{y}^{3}[/latex] 5. [latex]n[/latex] Solution| Polynomial | Number of terms | Type | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | [latex]8{x}^{2}-7x - 9[/latex] | [latex]3[/latex] | Trinomial |
| 2. | [latex]-5{a}^{4}[/latex] | [latex]1[/latex] | Monomial |
| 3. | [latex]{x}^{4}-7{x}^{3}-6{x}^{2}+5x+2[/latex] | [latex]5[/latex] | Polynomial |
| 4. | [latex]11 - 4{y}^{3}[/latex] | [latex]2[/latex] | Binomial |
| 5. | [latex]n[/latex] | [latex]1[/latex] | Monomial |
try it
[ohm_question]146073[/ohm_question]Determine the Degree of Polynomials
In this section, we will work with polynomials that have only one variable in each term. The degree of a polynomial and the degree of its terms are determined by the exponents of the variable. A monomial that has no variable, just a constant, is a special case. The degree of a constant is [latex]0[/latex] —it has no variable.Degree of a Polynomial
The degree of a term is the exponent of its variable. The degree of a constant is [latex]0[/latex]. The degree of a polynomial is the highest degree of all its terms.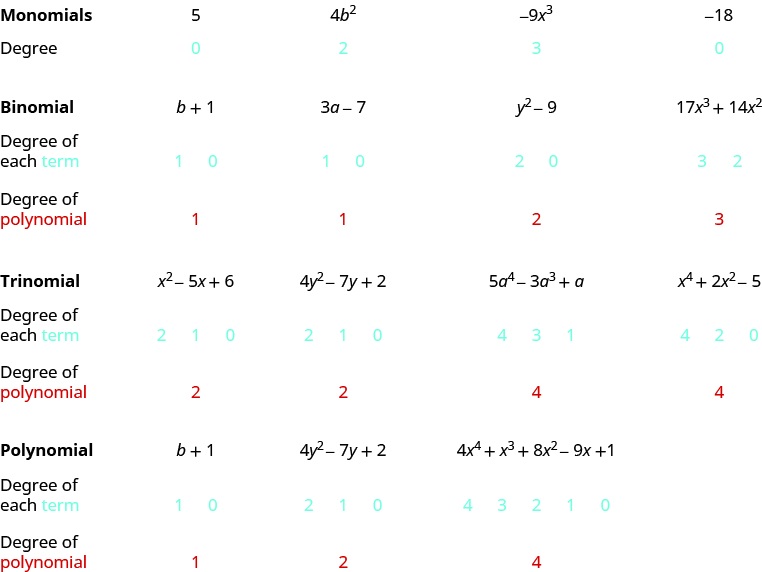
example
Find the degree of the following polynomials: 1. [latex]4x[/latex] 2. [latex]3{x}^{3}-5x+7[/latex] 3. [latex]-11[/latex] 4. [latex]-6{x}^{2}+9x - 3[/latex] 5. [latex]8x+2[/latex]Answer: Solution
| 1. | [latex]4x[/latex] |
| The exponent of [latex]x[/latex] is one. [latex]x={x}^{1}[/latex] | The degree is [latex]1[/latex]. |
| 2. | [latex]3{x}^{3}-5x+7[/latex] |
| The highest degree of all the terms is [latex]3[/latex]. | The degree is [latex]3[/latex] |
| 3. | [latex]-11[/latex] |
| The degree of a constant is [latex]0[/latex]. | The degree is [latex]0[/latex]. |
| 4. | [latex]-6{x}^{2}+9x - 3[/latex] |
| The highest degree of all the terms is [latex]2[/latex]. | The degree is [latex]2[/latex]. |
| 5. | [latex]8x+2[/latex] |
| The highest degree of all the terms is [latex]1[/latex]. | The degree is [latex]1[/latex]. |
try it
[ohm_question]146070[/ohm_question]Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Question ID 146070, 146073. Authored by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Specific attribution
- Prealgebra. Provided by: OpenStax License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected].
